What Are the Differences Between Kpop Generations? Story Behind of Each Era
What Are the Differences Between Kpop Generations? – Kpop, short for Korean pop music, has taken the world by storm over the past few decades. As the genre has evolved, distinct generations of artists have emerged, each with their own unique characteristics and contributions to the industry. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the differences between Kpop generations, tracing the evolution of this global phenomenon from its roots to its current status as a cultural powerhouse.
What Are the Differences Between Kpop Generations?

Understanding Kpop Generations
Before we dive into the specific differences between Kpop generations, it’s essential to understand what we mean by “generations” in the context of Kpop. These generations are not strictly defined by time periods but rather by shifts in musical styles, cultural impact, and industry practices. Each generation builds upon the foundations laid by its predecessors while introducing new elements that shape the future of Kpop.
The Concept of Kpop Generations
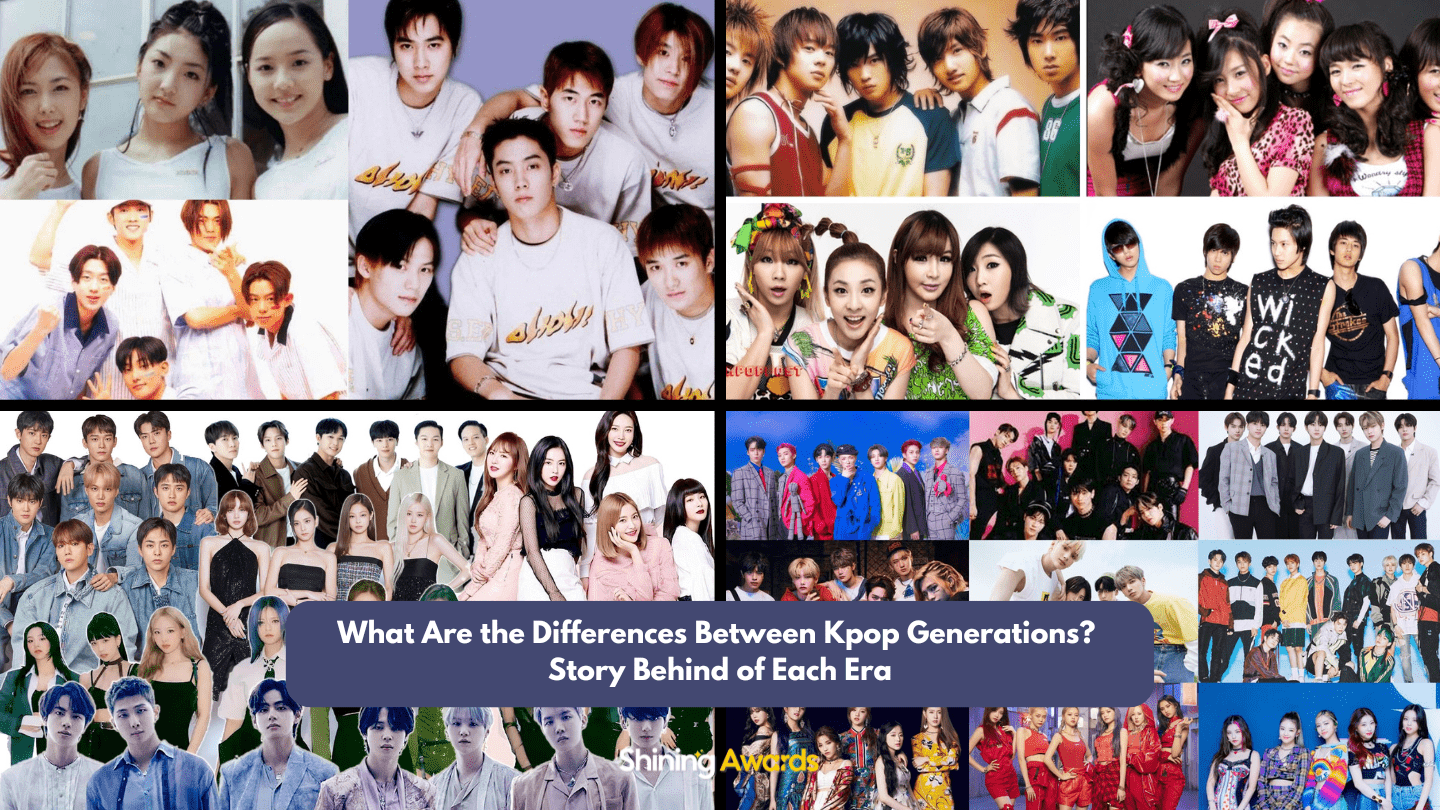
Kpop generations are typically categorized as follows:
- First Generation (1990s – early 2000s)
- Second Generation (mid-2000s – early 2010s)
- Third Generation (mid-2010s – late 2020s)
- Fourth Generation (late 2020s – present)
It’s important to note that these time frames are approximate, and there can be overlap between generations. Some artists may be considered transitional, bridging the gap between two generations.
Differences Between Kpop Generations: A Detailed Analysis
Now, let’s explore the key differences between Kpop generations, examining how each era has contributed to the evolution of the genre.
First Generation: The Pioneers of Kpop (1990s – early 2000s)
The first generation of Kpop laid the groundwork for the industry we know today. Here are some key characteristics of this era:
- Musical Style: Heavily influenced by American hip-hop and R&B
- Choreography: Basic dance routines, not as complex as later generations
- Fashion: Bright, colorful outfits inspired by Western pop stars
- Marketing: Primarily focused on domestic Korean market
- Notable Acts: Seo Taiji and Boys, H.O.T., S.E.S., Fin.K.L, g.o.d
Table: Key Features of First Generation Kpop
| Aspect | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Music | Hip-hop and R&B influenced |
| Dance | Simple choreography |
| Fashion | Colorful, Western-inspired |
| Target Market | Primarily domestic |
| Industry Structure | Emerging idol system |
Second Generation: The Global Breakout (mid-2000s – early 2010s)
The second generation of Kpop saw the genre begin to gain international recognition. This era is often considered the “Golden Age” of Kpop. Key differences include:
- Musical Style: More diverse, incorporating elements of electronic dance music (EDM) and pop
- Choreography: Increased complexity and synchronization in dance routines
- Fashion: Sleeker, more sophisticated styling with a blend of Korean and Western influences
- Marketing: Expansion into other Asian markets and the beginning of global outreach
- Social Media: Emergence of social media platforms for fan engagement
- Notable Acts: BIGBANG, Girls’ Generation, Super Junior, Wonder Girls, 2NE1, TVXQ, SHINee
List: Innovations of Second Generation Kpop
- Introduction of the “idol” concept
- Development of intricate fan cultures and fandoms
- Increased emphasis on visual elements in music videos
- Popularization of the “concept” approach to comebacks
- Establishment of the “Big 3” entertainment companies (SM, YG, JYP)
Third Generation: Global Domination (mid-2010s – late 2020s)
The third generation of Kpop saw the genre achieve unprecedented global success. This era is characterized by:
- Musical Style: Fusion of various genres, including trap, EDM, and traditional Korean elements
- Choreography: Highly complex and synchronized performances
- Fashion: High-fashion concepts and collaborations with luxury brands
- Marketing: Full-scale global promotions and world tours
- Social Media: Extensive use of social media for direct fan interaction
- Cultural Impact: Kpop becomes a significant part of the “Korean Wave” (Hallyu)
- Notable Acts: BTS, EXO, TWICE, BLACKPINK, Red Velvet, GOT7, SEVENTEEN
Table: Global Achievements of Third Generation Kpop
| Achievement | Example |
|---|---|
| Billboard Hot 100 #1 | BTS – “Dynamite” (2020) |
| YouTube Views Record | BLACKPINK – “DDU-DU DDU-DU” (1.5 billion+ views) |
| Stadium Tours | BTS – Love Yourself World Tour (2018-2019) |
| UN Speech | BTS at United Nations General Assembly (2018) |
| Grammy Nomination | BTS – “Dynamite” for Best Pop Duo/Group Performance (2021) |
Fourth Generation: Innovation and Individuality (late 2020s – present)
The current fourth generation of Kpop is still defining itself, but some emerging trends include:
- Musical Style: Experimental sounds, genre-blending, and increased artistic input from idols
- Choreography: Push for even more complex and visually striking performances
- Fashion: Bold, avant-garde styling and increased focus on individual members’ fashion
- Marketing: Utilization of AI and virtual reality technologies
- Social Issues: More open discussion of social and political issues
- Training System: Shorter training periods and debut through survival shows
- Notable Acts: ITZY, Stray Kids, TXT, ATEEZ, (G)I-DLE, ENHYPEN, aespa
List: Innovations of Fourth Generation Kpop
- Virtual idols and AI members (e.g., aespa’s ae-counterparts)
- Increased focus on storytelling and world-building in concepts
- Debut of groups through global fan-participated survival shows
- Greater emphasis on self-produced content
- Exploration of niche subgenres within Kpop
The Evolution of Kpop: Comparing Generations
To better understand the differences between Kpop generations, let’s compare some key aspects across all four eras:
Music Production
- 1st Gen: Primarily produced by a small group of in-house producers
- 2nd Gen: Introduction of international producers and songwriters
- 3rd Gen: Increased involvement of idols in music production
- 4th Gen: Emphasis on self-produced groups and individual member contributions
Training System
- 1st Gen: Relatively short training periods (1-2 years)
- 2nd Gen: Longer, more structured training (3-5 years on average)
- 3rd Gen: Highly competitive, extensive training (5-7 years or more)
- 4th Gen: Varied approach, with some groups debuting after shorter training periods
Fan Engagement
- 1st Gen: Fan clubs and physical album sales
- 2nd Gen: Online fan cafes and early social media interaction
- 3rd Gen: Extensive social media presence and global fan meetings
- 4th Gen: Virtual fan meetings, AI-enhanced interactions, and blockchain-based fan economies
International Reach
- 1st Gen: Primarily popular in South Korea
- 2nd Gen: Expansion into Asian markets
- 3rd Gen: Global recognition and charting on international music charts
- 4th Gen: Born into a globalized Kpop industry, with debut stages on U.S. TV shows
The Impact of Kpop Generations on the Global Music Industry
The evolution of Kpop through its various generations has had a profound impact on the global music industry:
- Innovative Music Videos: Kpop’s high-production value music videos have set new standards in the industry.
- Dance-Focused Performance: The emphasis on complex choreography has influenced Western pop acts.
- Fan Culture: The intense, engaged fan culture of Kpop has become a model for fan engagement worldwide.
- Social Media Strategy: Kpop’s effective use of social media has been adopted by many international artists.
- Training System: The rigorous training system has been studied and partially adopted by some Western labels.
Conclusion: The Continuing Evolution of Kpop
As we’ve explored the differences between Kpop generations, it’s clear that the genre has undergone significant changes since its inception. From its humble beginnings in the 1990s to its current status as a global cultural phenomenon, Kpop has consistently pushed boundaries and redefined what it means to be a pop music industry.
Each generation of Kpop has built upon the foundations laid by its predecessors while introducing new elements that shape the future of the genre. As we look to the future, it’s exciting to imagine how the current fourth generation and upcoming fifth generation will continue to innovate and expand the reach of Kpop.
The differences between Kpop generations are not just about changes in music style or fashion; they represent the evolution of an entire industry and cultural movement. By understanding these generational shifts, we can better appreciate the complexity and dynamism of Kpop as both an art form and a global force in entertainment.
Whether you’re a long-time fan who has witnessed the evolution of Kpop firsthand or a newcomer curious about the genre’s history, the story of Kpop’s generational progression is a fascinating journey through music, culture, and global influence.
